Legal Operations (or Legal Ops) is a multi-dimensional role that sits at the intersection of law with various other disciplines such as finance and budgeting, technology, risk management, project management, vendor management, knowledge management, data analytics, etc. Such roles tend to be more visible in an in-house set-up but law firms have had Chief Operating Officers or Chief Executive Officers who take over this role.
Legal Operations is a borrowed discipline. Its roots lie in Operations Management which is a field that focuses on maximising business efficiency through various processes that involve planning, prototyping, task management, organising, and outcome-based work delivery.
The primary flow of Operations Management is as follows:
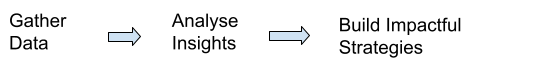
- Gather Data: Data gathering involves collating different sets of data from previous projects that a business has undertaken. These data sets could include employee’s performance, work time, efficiency, client satisfaction, costs, etc.
- Analyse Insights: Once data has been gathered and organised, it needs to be analysed, to make it useful for future references and increasing the overall efficiency of the business.
- Build Impactful Strategies: After analysing the data, it is used in a manner that strategies are built for future projects. These strategies aim to eliminate any encumbrances the data would have identified, and primarily builds tools and methods for greater results.
What is Legal Operations?
The Corporate Legal Operations Consortium (CLOC), a global community that aims to redefine business standards in law practice, describes Legal Operations as,
“a set of business
- processes,
- activities, and
- professionals
who enable legal departments to serve their clients more effectively by applying business and technical practices to the delivery of legal services. Legal ops provides,
- strategic planning,
- financial management,
- project management, and
- technology expertise
that enables legal professionals to focus on providing legal advice”.
According to the Association of Corporate Counsel (ACC), “Legal Operations is the function within the office of the general counsel that takes responsibility for efficient and effective delivery of legal services for the corporation. Dedicated legal operations staff focus on:
- optimizing how people, processes, and technology are deployed,
- leveraging data to inform decision-making and
- performance management.”
Why is a Legal Operations team essential?
A major chunk of the lawyers’ time is spent on documentation and administrative work. Manually keeping records of clients, tracking billing, managing, and communicating with vendors (including outside counsel) can come at the cost of inefficient legal services.
Legal Operations steps in as a department with transferred ownership of all administrative tasks and efficient business and technology application.
With this shift in responsibility, Legal Operations contributes in the following manner:
- Increases efficiency of lawyers in core legal practice (higher quality of legal work)
- Increases ability to form strong partnerships and propel inter-functional collaboration with various other departments such as finance, IT, HR, etc. This brings more capabilities to the project, maximizing the success rate.
- Brings more value to the table, by accelerating business through risk mitigation and strategic planning.
- Ensures resource efficiency for lawyers through various methods of knowledge management, latest technology tools support, etc.
- Helps in the growth of the business through regular data analytics by providing metrics and strategies for improvement.
Evolution of Legal Operations
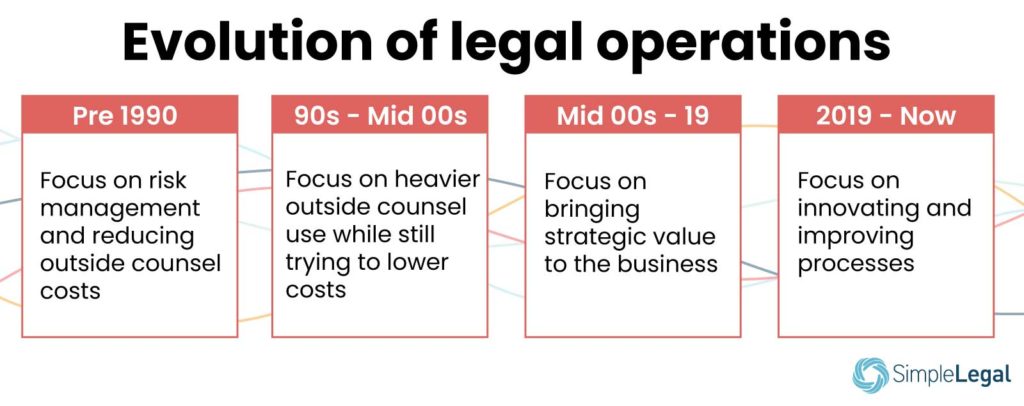
The pre-1990s were marked with first trying to reduce their vendors’ costs (outside counsel), and focused on risk management. The aim was to reduce the internal costs of the firm. Only a few firms had dedicated Legal Operations teams (eg: General Electric, Bank of America), the trend was still unheard of.
Post 1990s- 2000s were marked with similar efforts of reducing costs, but, outside counsel was relied upon, for efficiency and their strategic value.
The next two decades saw a shift in perspective, where firms focused on building value within the business, to avoid looking for assistance outside, this brought greater reliance on Legal Operations.
The present decade has seen a further shift in perspective, where innovation and efficiency is the main concern of a Legal Operations team. Newer strategies like technology adoption, automation, task management, cross-department collaboration, etc. are being adopted.
What is the role of the Legal Operations Team?
To best understand the role of the Legal Operations team, the CLOC has suggested a 12 core competencies model. Competencies are the different skills and abilities of a Legal Operations team, at different levels of expertise (Foundational, Advanced and Mature).
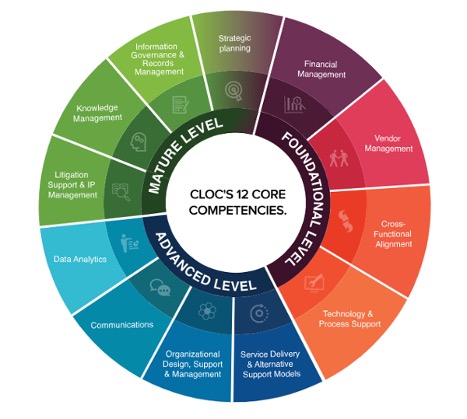
The CLOC Foundational Competencies include:
- Financial Management/ Budgeting: Manage departmental budget and work on cost-saving. They maintain financial reports for the legal department such as spending on vendors, technology tools and resources etc.
- Vendor Management: The Legal Ops team manages the procurement of external legal services (outside counsel, law firms), alternate legal services (IT management, contract drafting and life cycle management, staffing etc). They work on various tasks such as drafting and enforcing billing and fee requirements, communication with vendors, etc.
- Cross-Functional alignment: Maintain and propel relationships with other departments such as Finance, IT, HR, etc., to ensure that legal functions are performed most efficiently.
- Technology and Process support: Here, the role of the Legal Ops team is to automate functions such as contract management, compliance, research, billing etc, through Legal Tech. The Legal Ops team tracks new legal technology and analyses it as per utility. For a detailed guide on Legal Tech please visit our last post (linked here).
CLOC advanced competencies should be included once the foundational competencies have developed. These include:
- Service Delivery & alternate support models: This includes selecting right resources to reduce costs and develop a culture of automation. This is one with the support of alternate support models such as technology tools.
- Organisational, Design, Support & Management: Here, the role of the Legal Ops team is to ensure that a culture of growth and development exists in the organisation. Another role is to ensure that the performance of the team is collaborative within the organisation.
- Communications: Another role of the Legal Ops team is to ensure inter and intra communication. This would include tracking legal updates and developments with other organisations in the market and with the many other departments within the organisation.
- Data Analytics: Collect, analyse and store relevant data to strategize and gauge performances for future development.
CLOC Mature Level Competencies:
- Litigation Support and IP Management: Litigation support includes e-discovery, document review, etc. The other role is to provide operational support in IP-related matters.
- Knowledge Management: Here the role of the Legal Ops team is to ensure easy access to institutional knowledge. The team compiles and manages all information related to current case laws, rulings, legislations, etc to make it easy to locate and access information without spending time digging. Another manner in which the Legal Ops team helps manage knowledge is by creating templates contracts, pleadings, etc. The primary aim is to set up a centralised repository of legal documents and legislations.
- Information Governance and Records Management: Here the role is to record policies, processes and strategies of the organisation.
- Strategic Planning: Creating a long-term strategy, aligning yearly goals. Monitor whether goals are being met at the agreed timeframe and plan.
3 Levels of Legal Operations
As suggested by Association of Corporate Counsel (ACC), Legal Operations has three Levels:
Level 1: The Admin
- Beginner’s level
- Manages legal department vendors
- Basic reporting to stakeholders
Level 2: The Optimizer
- Focuses on Optimisation
- Reviews existing processes and determines which should be standardised and optimised.
Level 3: The Strategiser
- Cross-departmental work to ensure better efficiency.
Legal Operations Usecase – Anecdotal Evidence: Linklaters

How can I engage myself in Legal Operations?
To better understand how one can engage themselves in the Legal Operations department, we have attached a sample job description that you may refer to. Further, we have enlisted some reading materials, courses you may take, webinars and conferences you could participate in, podcasts you may stream, and people you may follow on a regular basis, in order to remain updated with the Legal Operations industry.
Legal Operations Job Roles
- Chief Legal Operations Officer
- Legal Operations Manager
- Legal Operations Specialist
- Legal Operations Analyst
- Director of Legal Operations
To know more about these specific job roles,visit, 4 examples of Legal Operations jobs to help you build your team, Simple Legal.
Sample Job Description

What should you read?
- What is Legal Operations? Corporate Legal Operations Consortium
- Learning Center, SimpleLegal (Articles, Guides, Templates, Videos, Product Data Sheets etc)
- Legal Operations eBook, Juro
- Resource Library, Association of Corporate Counsel
- Resources, Corporate Legal Operations Consortium (Guides & Templates, Surveys, Metrics & Reports, Vendor Directory, Access Institute Sessions)
- Library, UpLevel Ops (Articles, Guides, Templates)
- Legal Operations, Law.com
Streaming Content
- Legal Ops Rising, Podcast
- Legal Operations videos, CraftyCounsel
- Membership, Legal Operators
- Legal Operations: from nothing to something, Juro (Youtube)
People to follow
- Lucy Bassli, Legal Operations Consultant
- Praveen Cavale, Legal Operations – Business Analyst at Standard Chartered Bank
- Rachita Maker, Head of Legal Operations at Tata
- Mary O’Carroll, Former Director of Legal Ops, Technology and Strategy at Google Lens
- Colin S McCarthy, CEO and Founder at Legal Operators
- Stephanie Corey, Co-Founder at UpLevel Ops
Courses
- Legal Technology and Operations, Bucerius Law School
- Scholarship Program, CLOC
- Legal Innovation and Technology Certificate, Suffolk University
- Legal Operations, Practicing Law Institute
- Legal Operations, Vanderbilt Law School
- Legal Operations 2.0, Vanderbilt Law School
- Legal Practice Development and Management, Law Sikho
